CSR funding in India is projected to cross the Rs. 50,000 crore mark by March 2019 of which education and skills development projects are likely to benefit from Rs. 15,000 crores. We examine the changes in CSR spend on the basis of findings of the India CSR Outlook Report 2018 by CSR Box.
The business sense in adopting CSR are many. A higher brand value, more loyal staff, attracting investment as a socially responsible business and increased customer stickiness are just some of the reasons CSR should not be viewed as merely a social obligation. How does skills-based training fit into India’s CSR roadmap?
Section 135 of the Companies Act 2013 mandates companies with a net worth of Rs 500 crore or above, or an annual turnover of Rs 1,000 crore or above, or with a net profit of Rs 5 crore or more, to utilise 2% of their average net profit of the preceding three years on CSR activities.
The India CSR Outlook 2018 report has thrown up some interesting facts about corporate spending in the area. 359 ‘big’ companies were selected for an in-depth analysis of their CSR spend, all listed on the BSE or a subsidiary of a BSE-listed company. These companies make up approximately three-quarters of the total CSR spend in India, making them a good representational slice of the annual CSR pie and a strong indicator of current trends and activity in the Indian CSR landscape. Oil, drilling and petrochemical companies have contributed the most to CSR in the last year (23%), followed by banking & finance, and IT & ITeS.
Overall there has been a 2% increase in the actual CSR spend compared to 2016-17 translating into 25% more number of projects. A handful of big names have spent over their prescribed CSR budget with Reliance Industries topping the list. Other large companies that have gone above their prescribed CSR budgets for 2017-18 are HDFC Bank, Wipro, Tata Steel, NTPC, Indian Oil Corporation, and ONGC.
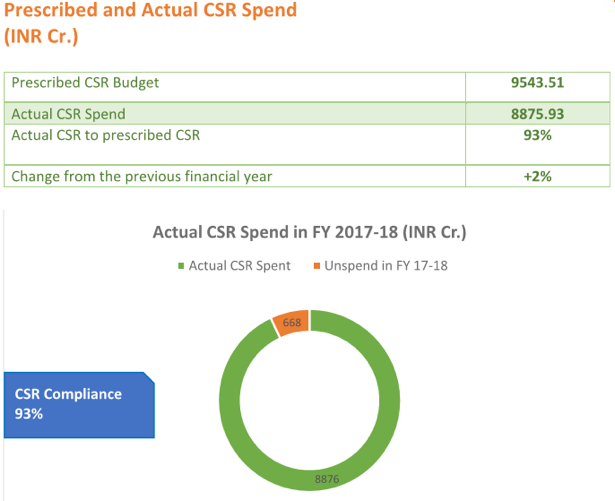

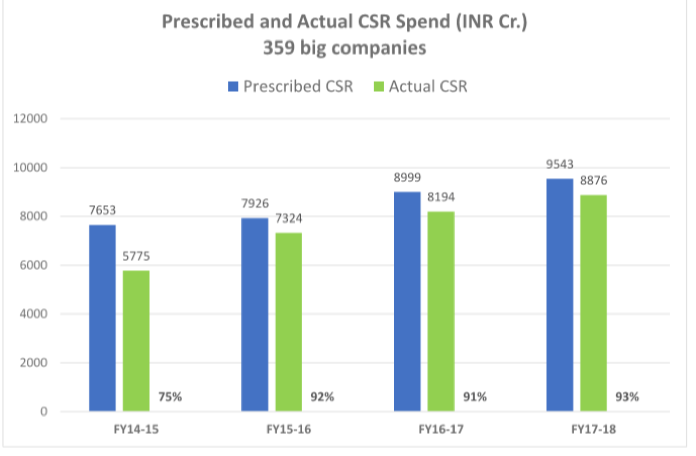
Year on year companies have been laying out more towards CSR in India, with a 24.7% increase in prescribed budget between 2014-2017, and an impressive 53.7% actual spend increase in CSR activities between the same period.

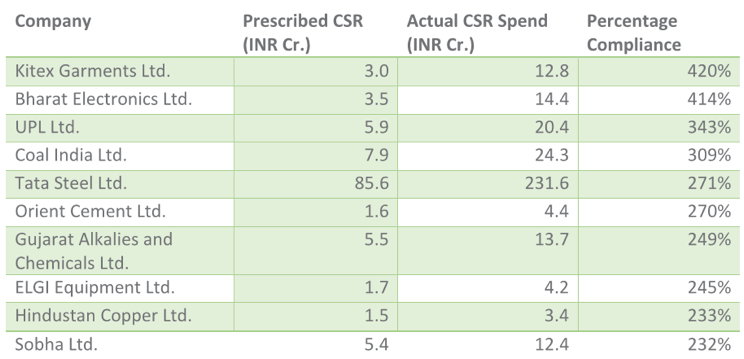
Outside of the top 10 companies in terms of actual CSR spend, a number of other companies have shown remarkable actual spend far beyond their CSR budgets with Kitex Garments Ltd at a 420% compliance rate, or 12.8 crores compared to a CSR budget of 3 crores. Similarly, Bharat Electronics Ltd., UPL Ltd., Coal India, and Tata Steel have all had impressive CSR outlays compared to their prescribed budgets. Such massive over compliance rates is yet another affirmation of the growing significance of CSR in corporate India.

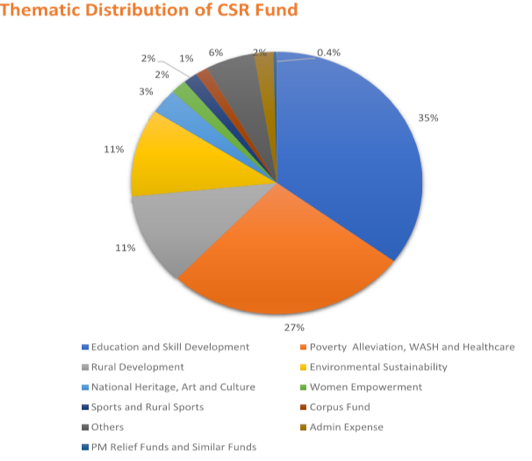
On the flip side deposits into the PM Relief Fund has seen an 80% nosedive between 2015-16 and 2017-18. We think the reasons could be many; companies increasingly want to be seen as socially and ethically responsible. Any organisation worth their salt have community projects built into their annual spend as a way to not only give back to society but also as a powerful tool for employee engagement into the overall ethos and culture of the organisation. Brands have become much more than just looking out for their bottom line. Another reason could be an emerging preference for companies to choose their own projects and areas of social development that tie in well with their own brands or employee interests or a mix of both. Having control over CSR projects in terms of choice and execution allows for a well-crafted and meaningful CSR program with full visibility.
Laying importance to skills training, education and skill development have emerged as the top choice for CSR spend. Over a third of the total outlay amounting to around Rs 3,121 crore in 2017-18 has been funneled into education and skill development, which is a massive 50% jump from 2015-16. CSR funding in India is projected to cross the Rs. 50,000 crore mark by March 2019 of which education and skills development projects are likely to benefit from Rs. 15,000 crores. This out show of enthusiasm towards skilling is an essential concerted step by industry recognising the crucial need to train the next generation of youth to meet massive human resource demand growth in every major sector.

Below is a list of 10 of projects undertaking the largest skill development initiatives under the CSR banner for 2016-2017, as reported by CSR Box:
Larsen and Toubro Limited
- Target: Youth between the ages of 18-35 years.
- How: 35.71 crores for construction skills training institutes
- Impact: 7000 youths from socio-economically backward backgrounds have been made employable
HDFC Bank Limited
- Target: Youth between the ages of 18-35 years.
- How: 18.40 crores for skills training with a focus on women and youth, through implementation partners.
- Impact: Nearly 16,000 individuals with support to a further 1,100 persons to become entrepreneurs
ICICI Prudential Life Insurance Company
- Target: Youth between the ages of 18-35 years with a special focus on women.
- How: 17.03 crores on skill development through ICICI Academy for Skills.
- Impact: Over 64,000 youth with 100% placement. In 2017 women trainees were 41% of the total 28,000 youth who received training. Tie up with 800 industry partners to absorb successful trainees into permanent employment.
NHPC Ltd
- Target: Youth between the ages of 18-35 years.
- How: 16.78 crores for skills training through ITIs
- Impact: Various vocational skills training projects confirming to the NSQF have been imparted to economically disadvantaged youth.
Idea Cellular
- Target: Youth between the ages of 18-35 years.
- How: 16 crores for TVET through implementation partners
- Impact: 10 training programs reaching out to 1800 youth in 6 States in wide-ranging skills such as electricians, mobile technicians, salon executives, logistics executives, retail store executives, among others.
Oil India Ltd
- Target: Unemployed youth between the ages of 18-35 years.
- How: 12.07 crores in skills-based training through MoUs with entities such as Construction Industry Development Council, Indian Institute of Entrepreneurship (Guwahati), Pragati Edutech (Guwahati), among others.
- Target: Unemployed Youth in the age group of 18-35 years.
- Impact: Between 2013 and 2017, 8,560 candidates have successfully completed training with a 78% placement rate. Additionally, 4,290 participants enrolled in various entrepreneurship education programs.
Maruti Suzuki India Limited
- Target: Unemployed youth between the ages of 18-35 years.
- How: 11.76 crores for skills-based training through 141 ITIs
- Impact: 144 students trained under the Maruti Suzuki training module have been offered permanent positions by Maruti Suzuki dealers
JSW Steel Ltd.
- Target: Unemployed youth between the ages of 18-35 years.
- How: 11.51 crores for skills training through ISO certified rural BPOs.
- Impact: 6000 individuals with nearly 280 women have been trained at the BPOs
Hindustan Petroleum Corporation Limited
- Target: Disadvantaged
- How: 11.48 crores for skills training through project Swavalamban’s ISO certified rural BPOs.
- Impact: Underprivileged youth have received training in diverse skill sets such as electrical, tailoring, welding, beautician and hospitality.
Mahindra and Mahindra Finance Limited
- Target: Youth between the ages of 18-25 years.
- How: 12.26 crores towards the KC Mahindra Educational Trust under 8 Mahindra Pride Schools across India imparting training to socially disadvantaged youth in ITeS, retail, and hospitality
- Impact: 100% placement of 25,092 students from all 8 locations
BOSCH India Ltd
- Target: School drop-outs from disadvantaged backgrounds between the ages of 18 and 25.
- How: 8.06 crores towards its BRIDGE CSR training program
- Impact: 100% job placement of 4,500 students
Conclusion
It is heartening to witness a massive uptick in education and skills-based training in the CSR agendas of big and medium-sized Indian companies. A trend that one hopes will continue with increased momentum as more stakeholders join the bandwagon to narrow the enormous skills gap in the Indian workforce across all major sectors. We have been examining various means of making vocational education more attractive and mainstream, as a way out for the unemployed youth. CSR is indeed one way to increase access to skills-based training. Given the enormity of the skill gap problem in the country in various sectors such as retail & e-commerce, logistics, tourism, beauty & wellness, or construction, skills-based initiatives need to move beyond a ‘side agenda’ of corporates to a more large-scale apprenticeship-based model.
References
- India CSR Outlook Report 2018, CSR Box, NGOBox
- A list of 10 big CSR projects in skills development in India (FY 2016-17)













